General Technical Information
- What is the Emulsion
- Comparison of particle size
- Characteristic of polymer emulsion
- Characteristic of polymer emulsion
- Physical and General properties of emulsion
- Purpose to use ethylene as monomer for copolymerization
- Composition and mechanical characteristic of EVA copolymer resin
- Plasticity effect of polyvinyl acetate by co-monomer
- Hydrolysis of film of vinyl acetate copolymer emulsion
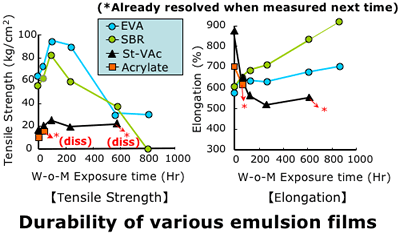
- Weather stability of EVA film by weather-o-meter
(20 hours/day, shower 18 min./120 min., 60±3 C)
1. What is the Emulsion
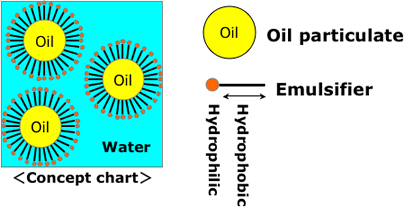
An emulsion is a mixture of two immiscible substances. One substance (the dispersed phase) is stably dispersed in the other (the continuous phase) by a dispersed effect of the surfactant.
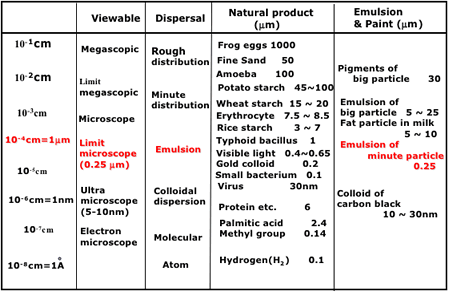
2. Comparison of particle size
3. Characteristic of polymer emulsion
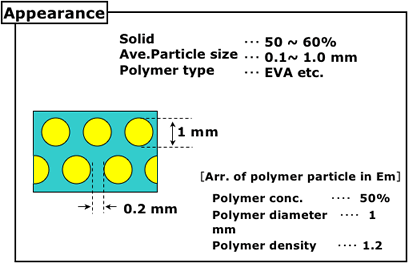
4. Characteristic of polymer emulsion
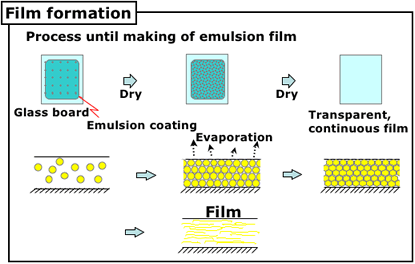
5. Physical and General properties of emulsion
Physical properties of emulsion
Solid content, Viscosity, pH,
Free monomer, Grits, Particle size,
Particle size distribution, Sedimentation,
Toluene insoluble parts, Tg, MFT
General properties of emulsion
- Safety (because the medium is water)
- Thixotropy fluid.
Share -> Low Viscosity
No share -> High Viscosity - Film formation
6. Purpose to use ethylene as monomer for copolymerization
- Internal plasticity effect
- Various polymer design
- Excellent water proof & alkaline resistance
- Excellent weather resistance
- Affinity with non-polarity material
(ex. plastic and synthetic material, etc.)
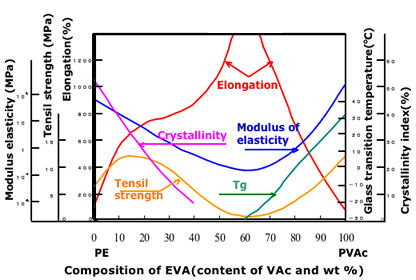
7. Composition and mechanical characteristic of EVA copolymer resin
8. Plasticity effect of polyvinyl acetate by co-monomer
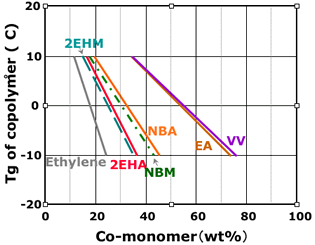
2EHM : 2-Ethylhexyl methacrylate, 2EHA : 2-Ethylhexyl acrylate
NBM : n-Butyl methacrylate, NBA : n-Butyl acrylate, EA : Ethyl acrylate
VV : Vinyl ester of Versatic (VeoVa)
9. Hydrolysis of film of vinyl acetate copolymer emulsion
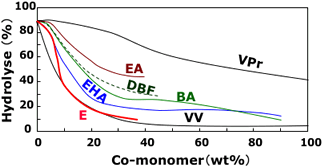
BA : Butyl acrylate, EA : Ethyl acrylate, EHA : 2-Ethylhexyl acrylate
E : Ethylene, DBF : Di-n-butyl fumarate, VPr : Vinyl propionate
VV : Vinyl ester of Versatic (VeoVa)
10. Weather stability of EVA film by weather-o-meter
(20 hours/day, shower 18 min./120 min., 60±3 C)